This post is also available in: 简体中文 (Chinese (Simplified))
The rolling mill for rails and sections of Aktobe Rail and Section Works LLP (ARBZ) is the first rail-manufacturing facility in all of Kazakhstan. Considered one of the world’s benchmark manufacturers of rails, it is based in the town of Aktobe, from where it caters to the growing demand of the domestic market and neighboring countries. Rails of up to 120 m in length are pre-certified according to the GOST standard, and are sold on the domestic market and exported to the Russian Federation as well as to CIS countries.
Under the auspices of Kazakhstan Temir Zholy JSC, the national railway company, the ARBZ venture was first established in 2012 and a decision was made to build the first rail manufacturing plant outside the city of Aktobe in the north-west part of the country, about 100 kilometers from the border with the Russian Federation. Aktobe is in a strategically favorable location, with easy access to markets in Europe, Russia, the CIS, and Middle East.
Primetals Technologies was awarded the main contract in 2013. Engineering, automation, and manufacturing took place in 2013 through 2014, and construction started in 2014. Hot commissioning started in September 2015, and the certification process was initiated in February 2016. The final plant acceptance certificate was signed in August 2017.
Plant layout and products
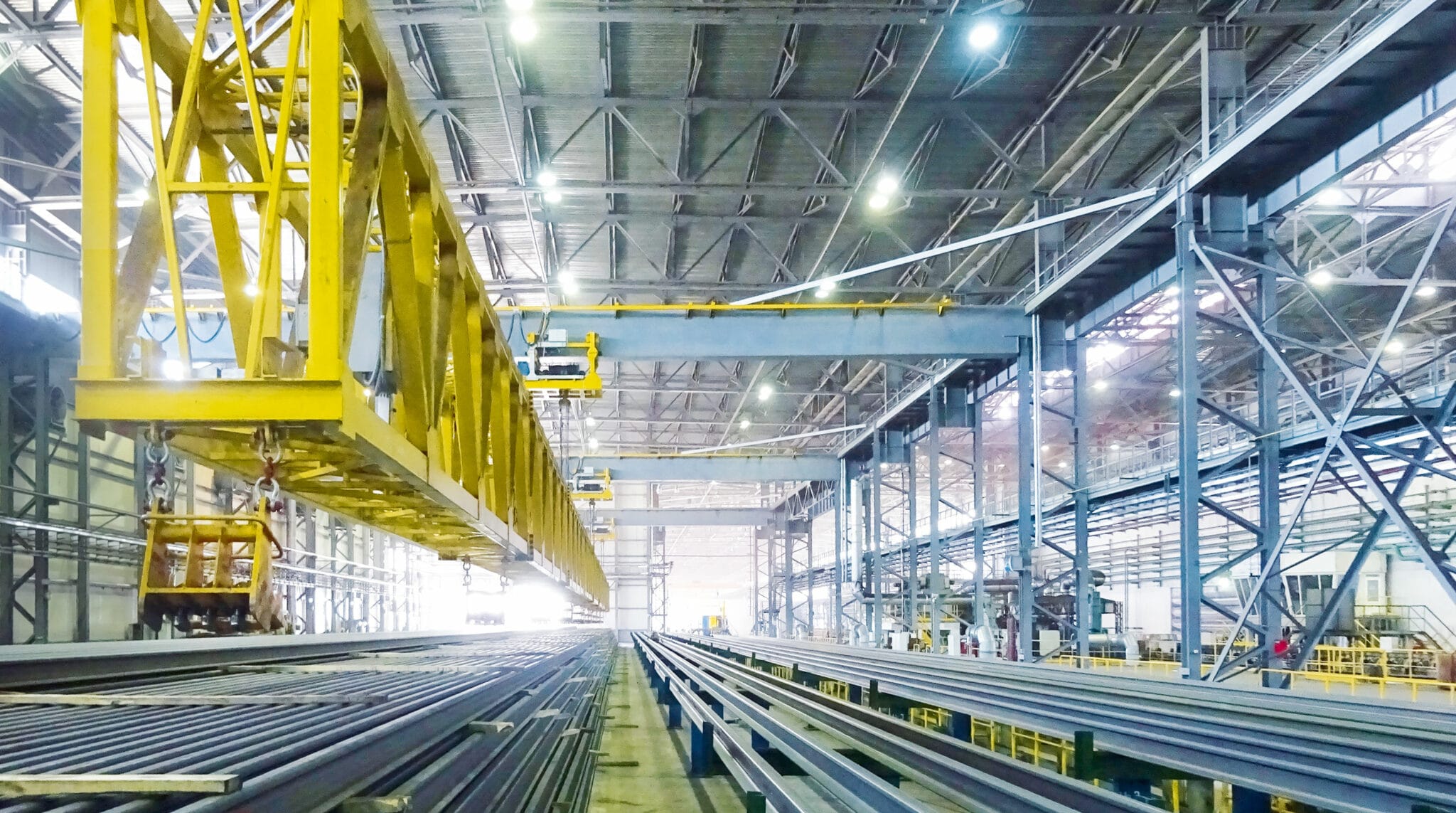
The ARBZ steel mill in Aktobe has a nominal production capacity of 430,000 tons per year. The overall footprint of the production area of the plant is 650 by 150 meters, remarkably compact for a facility designed to process long rails. In addition to some 200,000 tons per year of rails (P65 65 kg/m) in lengths of up to 120 meters, the product mix comprises 230,000 tons per year of structural medium sections, including beams and channels of up to 300 millimeters and angles of up to 200 millimeters. ARBZ is therefore able to flexibly react to changing market trends.
As the basic material, rectangular blooms with sizes of between 160 and 350 millimeters are used, with lengths ranging from 5 to 12 meters. The way in which the plant layout and equipment are configured allows for the expansion of the product mix to include additional rollable sizes, and for beam blanks to be used as the basic material. The re-heated bloom is rolled in a reversing breakdown mill and transferred to a reversing finishing mill for final rolling. Depending on requirements, rails may be head-hardened by Primetals Technologies’ patented Inline Injector Dual-Phase Rail Hardening System (idRHa+) before being deposited on the cooling bed. Cold rails and sections are straightened and then subjected to non-destructive tests before final handling and dispatch. Other included packages are the descaling systems, inline profile measurement, rail stamping unit, hot and cold saws for cutting and web drilling, laboratories, and a maintenance workshop.
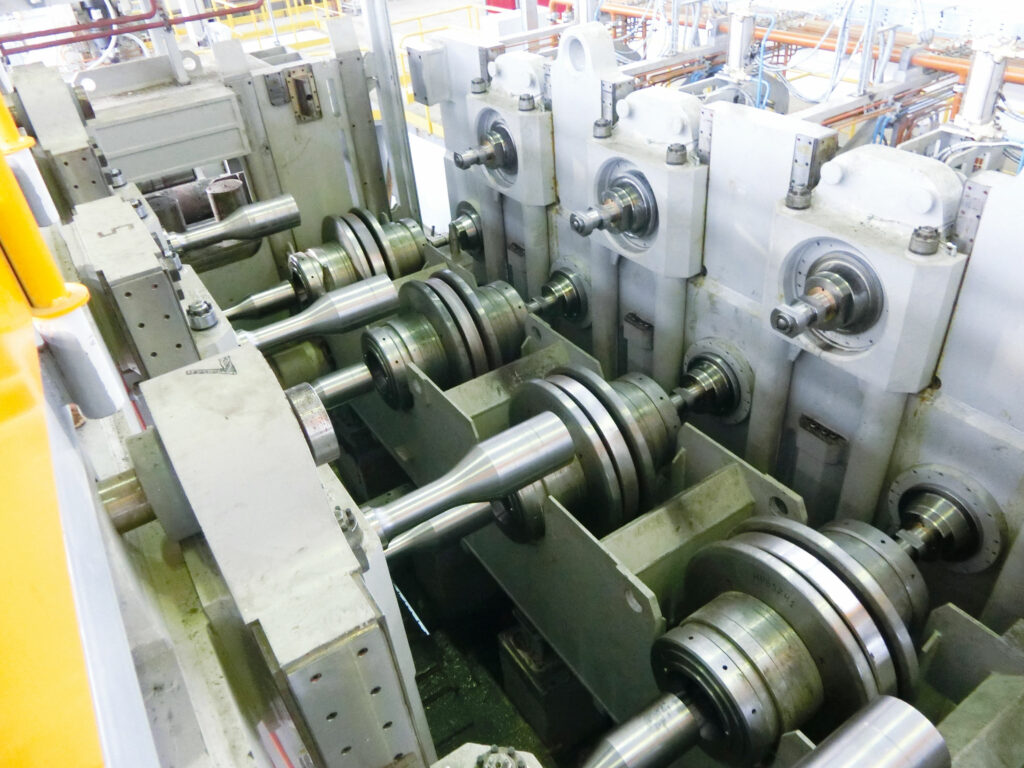
Reversing breakdown mill
The breakdown mill is a 2-high, reversing, housing-type machine with a roll-barrel length of 2,200 millimeters. The housing design provides the stiffness required to withstand the high separating forces with minimum deformation. The machine is equipped with automated lineals and tilters located at both entry and exit, which translate and rotate the bar in between the rolling passes and guide it into the selected groove.
Hydraulically balanced, the top roll is vertically positioned by a screw-down system, driven by two independent servo-controlled motors that automatically compensate possible asymmetries. The screw-down system is made of compound material with anti-friction coatings for increased wear resistance.
Hydraulic capsules are installed at the bottom of the machine to:
- adjust the centerline position of the bottom roll
- provide anti-jamming release functionality
- automatically position the bottom roll at the start of a roll replacement
- automatically control the rolling force
The innovative symmetrical open-pass calibration for rails ensures consistent dimensions of stock over the full bar length and reduces the risk of fin and wrinkle formation. At the same time, the guiding system is simplified and axial loads are reduced. The closed-pass calibration traditionally used for rails requires complex rolling sequences and bulky guide equipment with side collars that limit usable barrel length. By relying on symmetrical open-pass calibration instead, the rolling sequences are simplified and the bar is simply and effectively guided by the lineal noses and shoe plates. The full roll-barrel length can thus be utilized and rolls with smaller barrel and diameter can be used. Uniform groove wear is ensured, while roll lifetime is increased and redressing times are reduced.
When manufacturing the P65 rail from a 360 by 300 millimeter bloom, the breakdown mill applies nine rolling passes to the bloom and shapes it to a leader section. The first six passes are high-reduction box-type and guarantee the desired metallurgical properties in terms of grain size and core soundness; the final three passes are shape-type and allow for the precise leader pass required to feed the finishing mill.
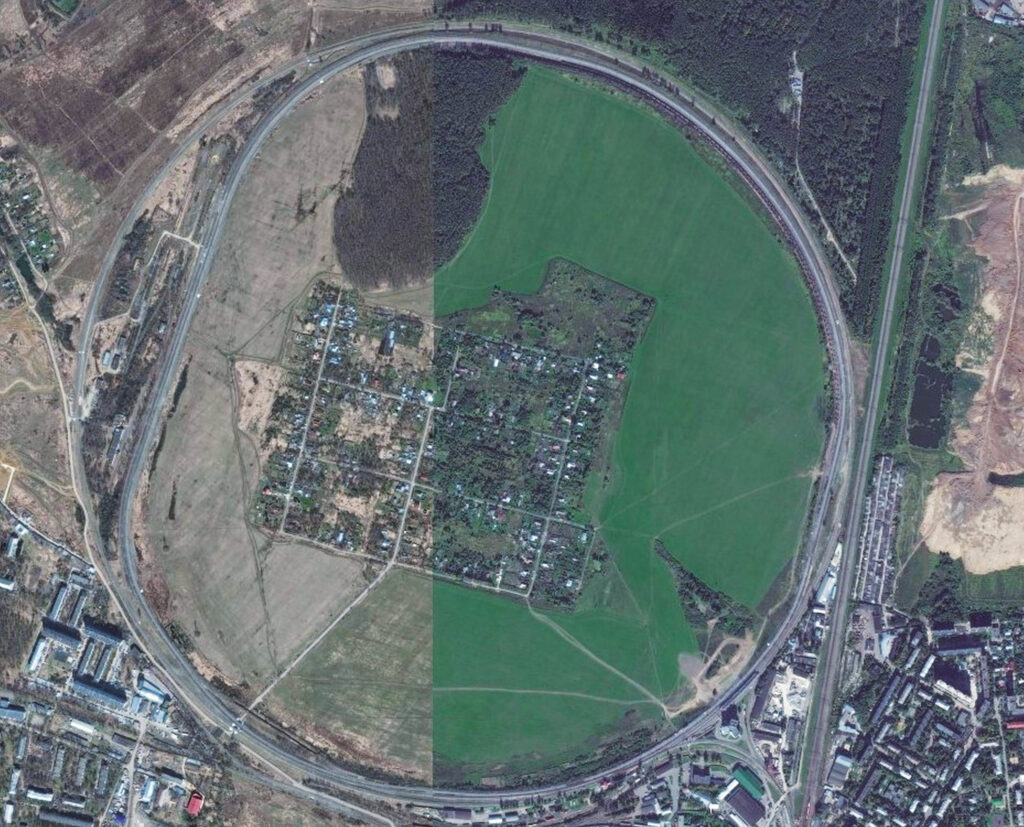
National certification in line with Kazakh standards was completed in a very short time, as the project scope included the in-house certification laboratory. ARBZ then began the multi-year certification process according to the Russian GOST standard, and pre-certification was obtained in November 2016 after a rigorous six-month testing protocol at the All Russian Railway Research Institute (VNIIZhT). VNIIZhT operates a railway loop where the rails are tested and a variety of operating conditions are simulated, such as train composition, load distribution, time, acceleration, speed, braking, and gradient.

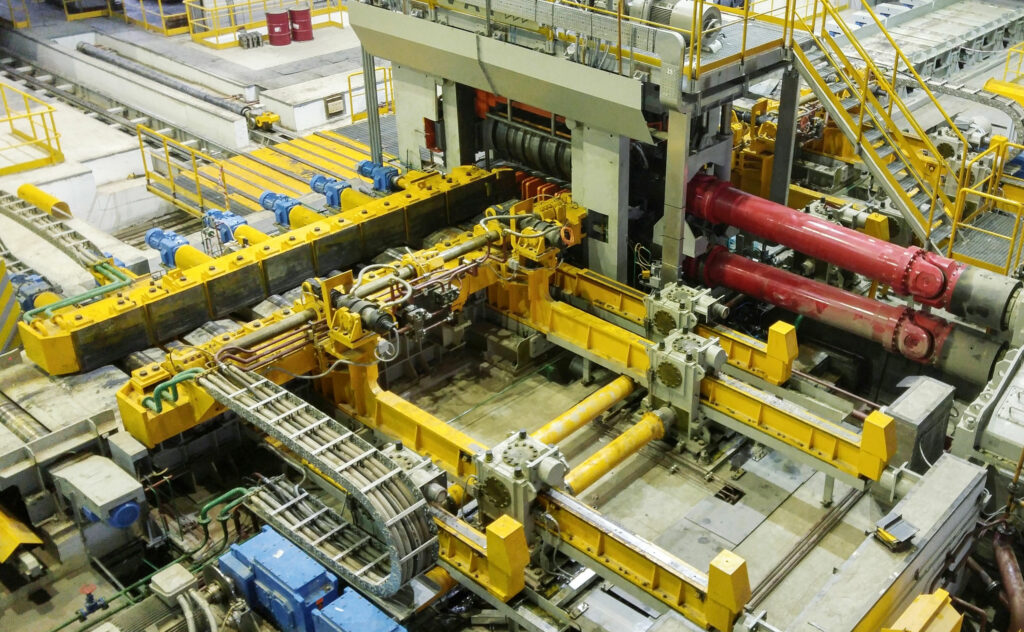
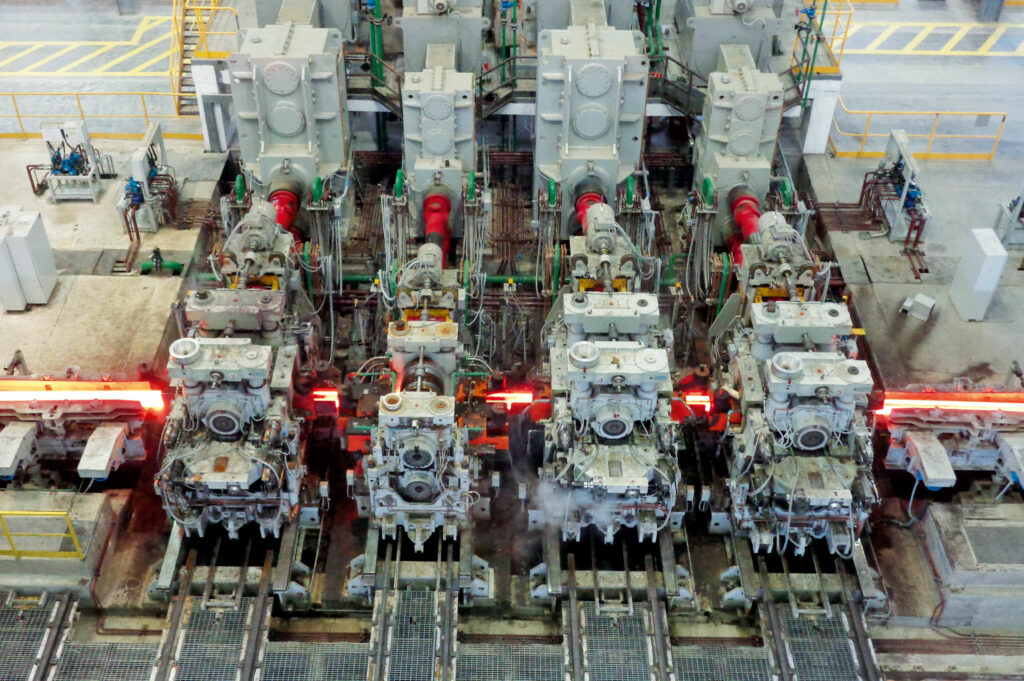
Universal finishing tandem mill
After the breakdown mill, the bar is cross-transferred to separate the rolling between roughing and finishing, and to limit the plant’s footprint. The universal finishing tandem mill is made up of four stands of the fourth-generation housingless Red Ring type, with solid and compact construction for high load capacity, wear-resistance, and ease of maintenance.
The stands can be quickly converted from universal to horizontal configuration and vice versa. The universal configuration is used for rolling rails, beams, and channels, while a full horizontal configuration is used when rolling angles.
Whenever spare units that have been prepared in the roll shop are used, total downtime can be kept below 30 minutes. Offline in the workshop, the stand parts (horizontal rolls, vertical rolls, chocks, baseplate) are disassembled and reassembled with dedicated automated jigs.
The 3+1 finishing mill uses a particular sequence with three reversing runs to process the leader pass prepared by the symmetrical calibration of the breakdown mill. The reversing runs allow precise control of the bars’ temperature and of the temperature’s head-to-tail gradient. During the first two reversing runs, the fourth finishing stand stays open and is not used. It is only closed during the third run, once on each bar, applying a small finishing reduction.
In comparison to a traditional 3-stand finishing mill, the rolls at the fourth stand of the 3+1 mill are subjected to lower stresses and will show reduced wear. They need to be serviced less frequently, which makes changes largely unnecessary: one roll set can typically be used for a full campaign. Available hours and productivity are thus increased, and the return on investment for the fourth stand is short. The small-reduction finishing pass improves surface smoothness and size accuracy, which is especially beneficial when special-class products are rolled, e.g. X-class rails.
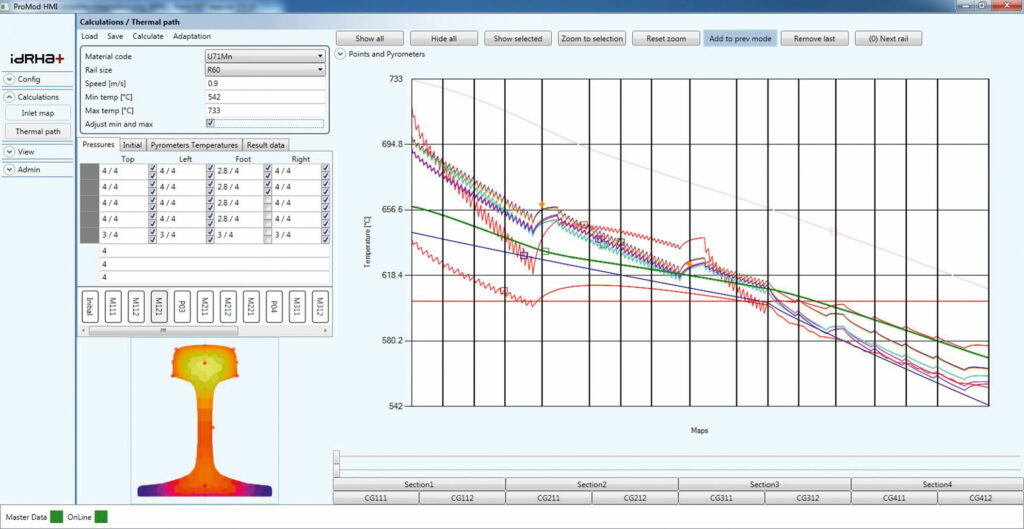
idRHa+ inline rail hardening
In order to produce rails with a high resistance to rolling-contact fatigue and wear, the mill at ARBZ is equipped with Primetals Technologies’ patented Inline Injector Dual-Phase Rail Hardening System (idRHa+). idRHa+ is based on a software suite that comprehensively simulates the production process by modeling the transfer of thermal energy to the rails, as well as the change of their mechanical properties and the transformation of their metallurgical structures. The application of idRHa+ leads to required hardness distribution across the full rail section, as well as to a consistent microstructure.
The heating zone is equipped with a set of high-power induction modules for immediate heat transfer. The heating action equalizes the temperature of the rail along its length and applies the desired temperature gradient over its cross-section.
The cooling zone contains several independent modules, each equipped with a set of interchangeable cooling devices that apply the required cooling protocols. Mist-water atomizers and air-jet blades are used. Modules are independently operated to remain flexible in terms of changing the optimum cooling protocol application. Cooling speeds can range from 0.5°C/s to 40°C/s. Rails processed with idRHa+ are then brought into a head-up position and sent to the cooling bed, where they are not prone to bulging.
The role of rail transport, both passenger and freight, is becoming increasingly important throughout the world. The global rail market posted an annual growth rate of 3% in 2013 through 2015, and is forecast to continue growing steadily until 2021, when the market is expected to reach 218 billion dollars.
To meet the demands of higher speeds and high loads, all the major national rail material standards were updated in the period from 2010 to 2015. Quality must be raised to much higher levels than was considered adequate at the end of the 20th century. Manufacturing units are expected to efficiently produce rails in a wide range of grades, sizes, and lengths, with mechatronically assisted setup procedures and self-adapting operations governed by process control. These are the tenets of Industry 4.0 that will promote digitalized manufacture, with considerable benefits in terms of product quality, shorter start-up times, lower running costs, greater operational flexibility, and the efficient use of resources.

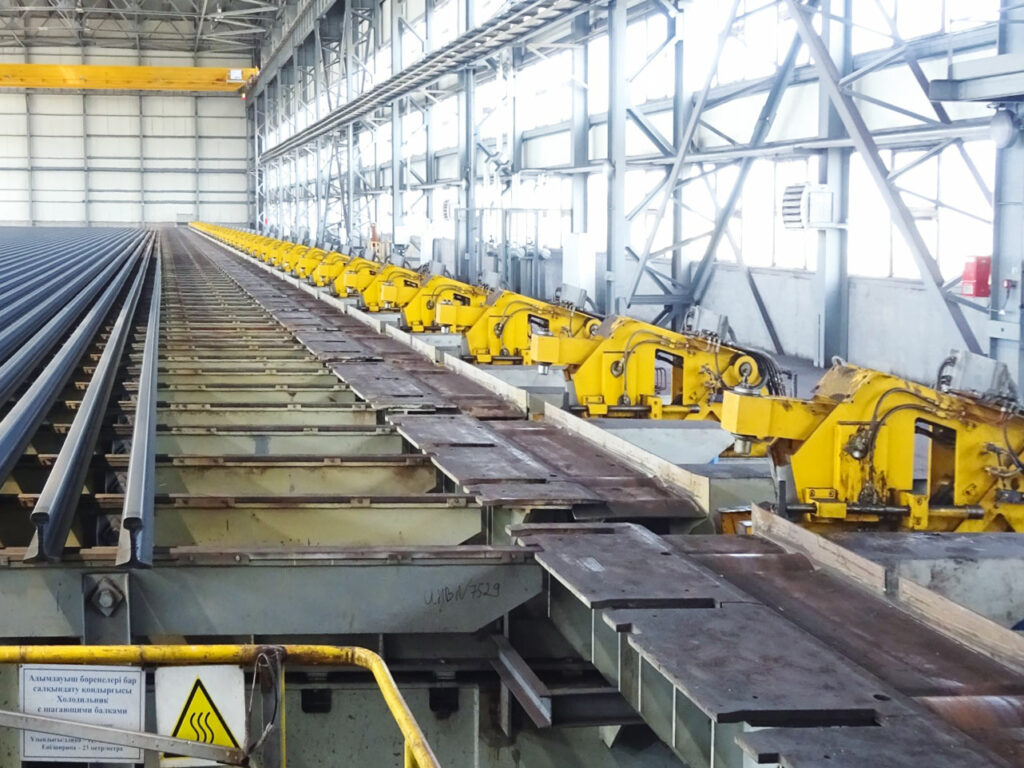
The cooling bed
The mill is equipped with a 125-meter walking-type cooling bed, capable of handling rails with a maximum length of 120 meters. The cooling effect is by natural air flow. On the cooling bed, non-hardened rails tend to bulge inward on their head side due to differential cooling gradients in the section. In order to prevent distortion and internal stresses, Primetals Technologies installed a pre-cambering system at the bed inlet table that applies a controlled outward bulge on the rail. 3-meter-spaced hydraulic grippers are mounted on independently traveling cars to apply the desired pre-camber according to a calculation model.
Straightening systems
The combined effects of the mechanical work from rolling and of inhomogeneous cooling result in considerable internal stresses on the product at the cooling-bed exit. International standards dictate acceptable limits for the internal stresses in order to prevent any distortions in the final product. Inline roll straightening is the last process of plastic deformation along the chain of production. The straightening process involves the application of calculated and controlled plastic deformations along the bar length. During straightening, the internal stresses are reduced to within an acceptable range, while precise straightness tolerances are achieved.
For structural sections, there is a horizontal multi-strand straightener with nine double-supported staggered rolls. For rail straightening, one horizontal and one vertical machine are used, which act on the rail head and foot, and on the rail web, respectively. The horizontal straightener, with nine individually driven rolls, is equipped with hydraulic capsules with digital pressure and position transducers. The mechatronic control precisely adjusts roll position under load and in real time.
Successful project execution
Primetals Technologies completed the rolling-mill project in August 2017, when the final acceptance certificate for the rolling mill was signed. However, the partnership between Primetals Technologies and ARBZ is set to continue: the two companies have since entered into a long-term agreement for spare-part supply in order to maximize plant availability. This will ensure that ARBZ will optimally contribute to the improvement of Kazakhstan’s rail infrastructure for many decades to come.
idRHa+ stands for “Inline Injector Dual-Phase Rail Hardening System” and is based on an advanced software package that comprehensively simulates the production process. The suite integrates with the equipment’s advanced sensors and mechatronics, thus implementing Industry 4.0 production management solutions. The models allow for the prediction and real-time control of the rail properties along the length and across the section, such as YTS, UTS, hardness gradient, microstructure transformation, and deformation behavior. The cooling protocols provided by the models are applied by the equipment modules, which are located inline with the finishing rolling operation, so that productivity is not affected. The real-time measured values are used to dynamically adjust the process and the equipment. As a result, the desired microstructure and hardness distribution across the rail section is kept consistent.