New technologies have emerged that are redefining production. With an increased demand for steel, these technologies provide an opportunity for sustainable transition while increasing performance and yield. Metals production is being redefined as production routes shift toward direct reduction and electrification.
While the BF-BOF production route dominates the steel industry, the realities of this route present tremendous opportunities for sustained success. In a cycle of approximately every fifteen years, blast furnace relining occurs. With about 70 percent of all blast furnaces requiring relining by 2030, producers can decide whether to reinvest in the blast furnace or to convert their production toward green steel. The time to transition toward green steel is here.
Transforming Raw Materials
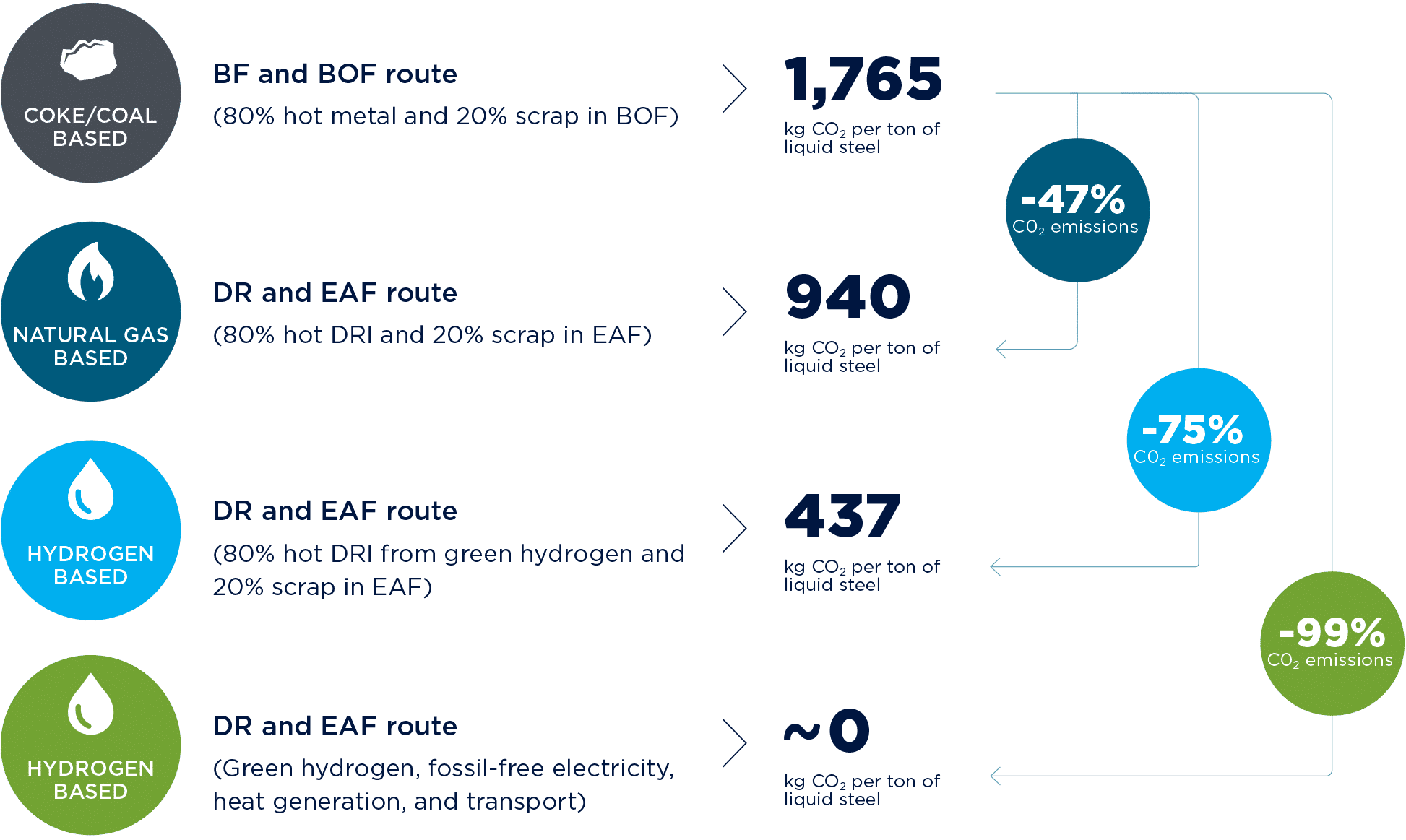
The blast furnace is one particular focus of the transition toward green steel, the most significant contributor to carbon emissions in the steel industry. However, despite the challenges associated with replacing the blast furnace, innovations for the direct reduction of iron ore offer immediate emissions reduction opportunities. New emergent technologies can accelerate a return on investment to make direct reduction a key part of a plant’s transformation.
The MIDREX direct reduction process has gained traction worldwide as one of the most standard processes for the direct reduction of iron ore with immediate benefits for the reduction of CO2 and the production of high-quality merchant hot-briquetted iron (HBI). HBI is a valuable material due to its ability to be easily transported worldwide, implemented in existing integrated steel plants, and used in electric steelmaking. Moreover, a MIDREX direct reduction plant operating entirely on natural gas significantly reduces overall emissions compared to a blast furnace. Capable of 100 percent hydrogen operation, MIDREX plants can transition as the hydrogen economy expands.
Steel Production with Low-Grade Iron Ore
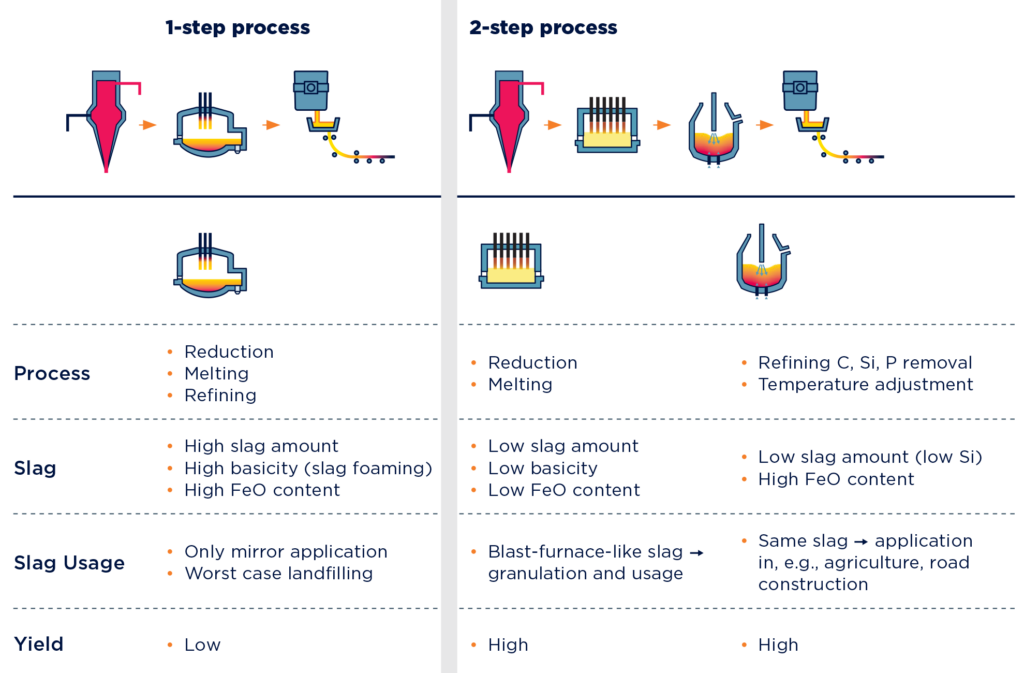
With immense numbers of direct reduction plants to be built in the coming years, one additional challenge for producers is the low amount of high-grade iron ore on the market. The Smelter, an innovation for melting low-grade hot charged direct reduced iron, was developed to take advantage of an increased amount of low-grade iron ore on the global market. (Read more about the Smelter in “Green Hot Metal: Introducing the Smelter“) With liquid hot metal coming from melting low-grade direct reduced iron in the Smelter, producers can take advantage of direct reduction’s carbon emissions reduction capabilities while still operating a BOF-dominant meltshop. Operating on electricity, the Smelter is also a characteristic sign of further transformation in the industry—the electrification of production.
Readily Available Technologies
Electrification of Production
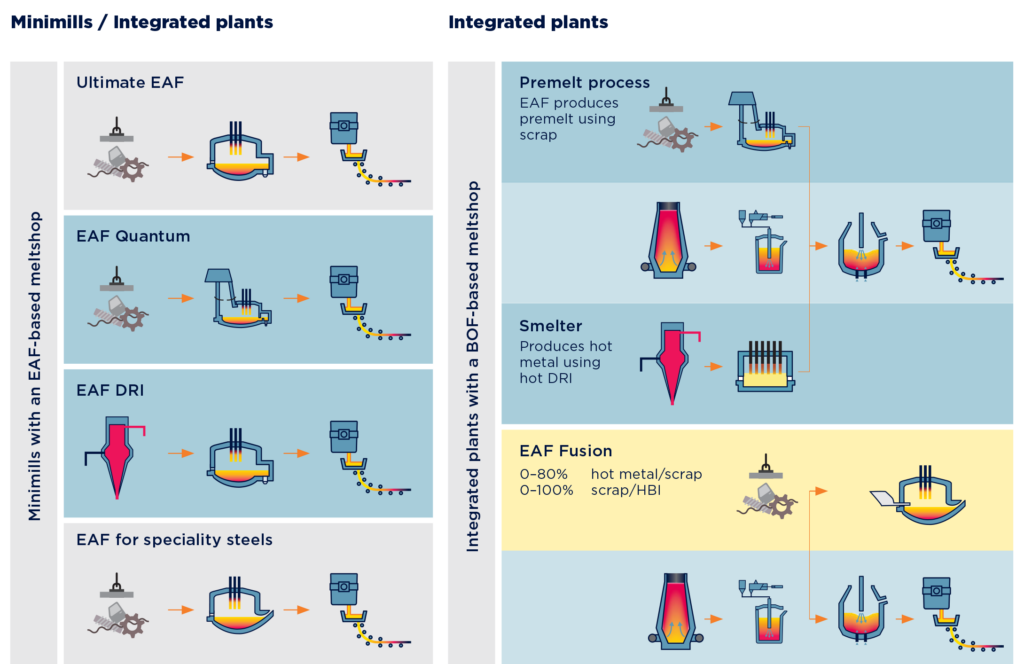
Today, scrap-based electric steelmaking offers producers the most environmentally friendly means of steel production. One key consideration for producers implementing and transitioning to electric steelmaking is incorporating an electric arc furnace into existing meltshops, replacing a BOF. By investing in electric arc furnaces while continuing operation with existing assets, producers can cater to and anticipate any necessary changes to plant logistics. Once online, the electric arc furnace can take on the lion’s share of steel production, lessening the impact of replacing further BOFs. With an EAF online, producers can immediately take advantage of the environmental advantages, including 100 percent scrap charging and increased direct reduction.
Primetals Technologies has two primary electric arc furnaces for the transition to electric steelmaking: the EAF Ultimate and EAF Quantum. Each with similar advantages, including fast tap-to-tap time and proprietary automation solutions for efficient energy regulation, these electric arc furnaces are oriented toward a sustainable steel industry. The EAF Quantum also features scrap preheating, making it ideal for scrap-based steelmaking. With shifts toward electric steelmaking on the horizon, capacity and energy consumption are primary concerns for which these electric arc furnaces meet the capacity demands of the industry while maintaining energy efficiency.
EAF Emissions Reduction Potential
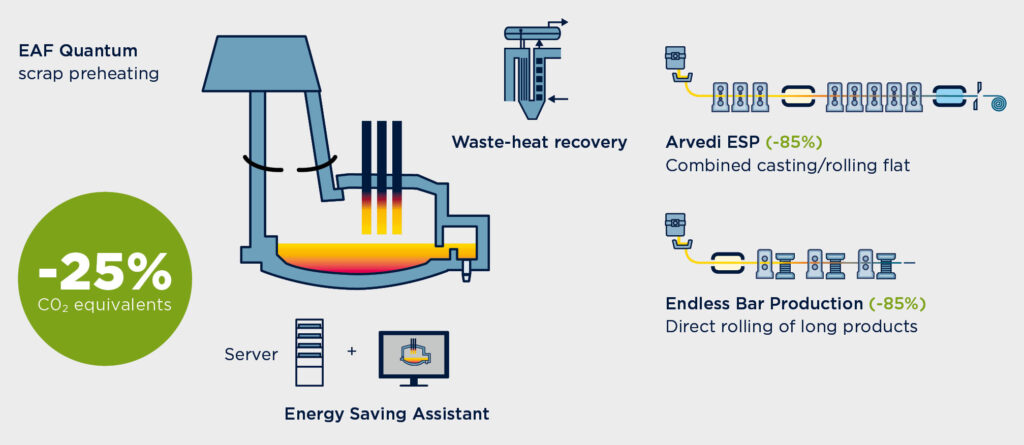
such as Arvedi ESP, reveals immediate potential for emissions reduction.
Streamlining Quality End Products
Whether incorporating changes into the raw material value chain or the meltshop itself, downstream production processes, such as continuous casting and rolling, present further immediate improvement opportunities. Fulfilling the Best Available Technologies requirements for near-net shape casting, Arvedi ESP is the most advanced, energy-efficient, and compact means of immediate casting and rolling of direct application end products. The process effectively shortens the entire production chain, allowing producers to go from liquid metal to rolled end products in record time with less energy consumption and in an ultra-compact format, removing additional reheating steps.
Arvedi ESP benefits from nearly fifteen years of references and experience to become a reliable solution for hot-rolled end products. For revamping projects or producers looking to build efficient plants by integrating direct reduction, electric steelmaking, and endless strip production (ESP), the possibility to transform production routes comes with lucrative opportunities to meet growing demands for high-quality steel, while securing one’s position on the global market by avoiding setbacks incurred through rising prices of carbon emissions certificates and the implementation of carbon taxes.
From Industry Trend to Reality
These improvements represent ideal opportunities for leading producers to gain a competitive edge. They redefine steel production and lay the foundation for a carbon-neutral steel industry. As global shifts toward sustainability impact various industries, including e-mobility, renewable energy, and hydrogen, the metals industry is in a key position to turn a global trend into reality. By investing in these transformative technologies, the global metals industry can serve as a model of how heavy industry can reach carbon neutrality and achieve green steel.
Comparison of Emissions between Routes